Cryptocurrencies’ popularity is growing despite short-term fluctuations. Peer-reviewed research into trust in cryptocurrency payments started in 2014 (Zarifis et al., 2014, 2015). While the model created then is based on proven theories from psychology, and supported by empirical research, a-lot has changed in the past 10 years. This research re-evaluates and extends the first model of trust in cryptocurrencies and delivers the second extended model of consumer trust in cryptocurrencies CRYPTOTRUST 2 (Zarifis & Fu, 2024) as seen in figure 1.
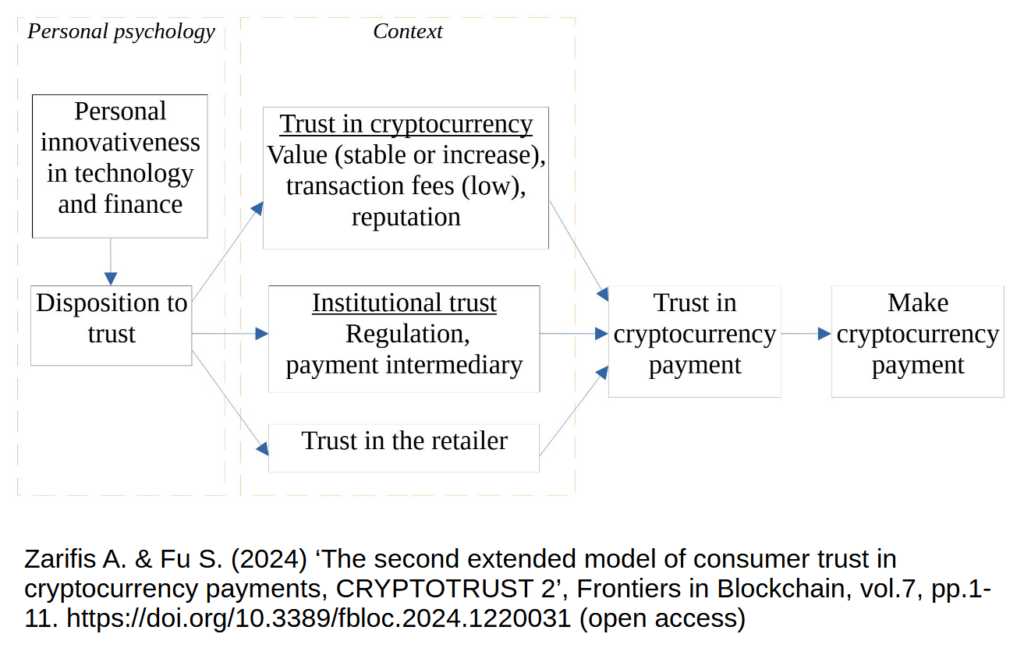
Trust in a cryptocurrency is a multifaceted issue. While some believe that the consumer does not need to trust cryptocurrencies because they utilize blockchain, most people appreciate that you must trust cryptocurrencies, just as you must trust any other technology you use that involves some risk.
The first three variables of the model come from the individual’s psychology: Personal innovativeness is divided into (1) personal innovativeness in technology and (2) personal innovativeness in finance. These two influence (3) personal disposition to trust.
There are then six variables that come from the specific context, and not the person’s psychology: The first three are related to the cryptocurrency itself. These are (4) the stability in the cryptocurrency value, (5) the transaction fees and (6) reputation. Institutional trust is shaped by (7) regulation and (8) payment intermediaries that may be involved in fulfilling the transaction. The last contextual factor is (9) trust in the retailer. The six variables from the context influence (10) trust in the cryptocurrency payment which then, finally, influences (11) the likelihood of making the cryptocurrency payment.
Separating personal innovativeness to personal innovativeness in (1) technology and (2) finance, is a useful distinction as some consumers may have different levels of personal innovativeness for technology and finance. The analysis here supports that these are separate constructs.
This research shows that trust in cryptocurrencies has not changed fundamentally, but it has evolved. All the main actors in the value chain still play a role in building trust. There is more emphasis from the consumer on having a stable value and low transaction fees. This may be because consumers now have more experience with cryptocurrencies, and they are better informed. It may also be because there are more cryptocurrencies available, and other alternatives such as Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC), so consumers can review the many alternatives and try to identify the best one.
References
Zarifis A., Cheng X., Dimitriou S. & Efthymiou L. (2015) ‘Trust in digital currency enabled transactions model’, Proceedings of the Mediterranean Conference on Information Systems (MCIS), pp.1-8. https://aisel.aisnet.org/mcis2015/3/
Zarifis A., Efthymiou L., Cheng X. & Demetriou S. (2014) ‘Consumer trust in digital currency enabled transactions’, Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing-Springer, vol.183, pp.241-254. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11460-6
Zarifis A. & Fu S. (2024) ‘The second extended model of consumer trust in cryptocurrency payments, CRYPTOTRUST 2’, Frontiers in Blockchain, vol.7, pp.1-11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbloc.2024.1220031 (open access)

